The Ultimate Guide to Fullstack Web Development
Fullstack web development encompasses the complete spectrum of a web application’s development, from creating a stunning user interface to managing server-side logic and databases. It involves mastering both frontend and backend technologies, allowing developers to build fully functional web applications from start to finish. Let’s dive into the key components and tools involved in fullstack web development.
What is Fullstack Web Development?
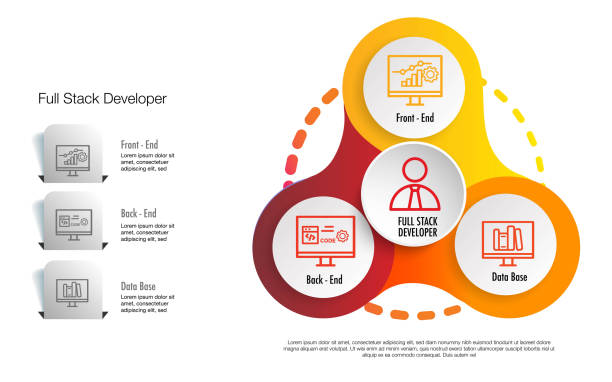
Fullstack web development refers to the practice of working with both the frontend and backend aspects of a web application. A fullstack developer is proficient in:
- Frontend Development: The part of a web application that users interact with. This includes designing and implementing the user interface using technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Backend Development: The server-side logic and database management that power the frontend. This involves working with server languages like Node.js, Python, Ruby, and handling databases using SQL or NoSQL technologies.
The Role of a Fullstack Developer
A fullstack developer wears many hats. They’re involved in all stages of development, from brainstorming ideas and designing the UI/UX to coding the backend logic and deploying the application. Key responsibilities include:
- Designing responsive and dynamic user interfaces.
- Developing server-side logic and integrating it with the frontend.
- Managing databases, ensuring data is stored and retrieved efficiently.
- Ensuring cross-platform compatibility and optimizing application performance.
- Collaborating with designers, product managers, and other stakeholders to deliver a seamless user experience.
Essential Frontend Technologies
 1. HTML (HyperText Markup Language)
1. HTML (HyperText Markup Language)
HTML is the backbone of any web page. It structures the content, defining elements like headings, paragraphs, links, and images. Mastering HTML is the first step towards becoming a proficient fullstack developer.
2. CSS (Cascading Style Sheets)
CSS is used to style HTML elements, controlling layout, colors, fonts, and overall visual appeal. Modern CSS frameworks like Bootstrap and Tailwind CSS offer pre-designed components, speeding up the development process.
3. JavaScript
JavaScript adds interactivity to web pages. From simple form validations to complex single-page applications (SPAs), JavaScript is indispensable. Popular libraries and frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.js further enhance its capabilities.
Key Backend Technologies
1. Node.js
Node.js allows JavaScript to run on the server-side. It’s known for its event-driven, non-blocking I/O model, which makes it ideal for building scalable network applications. Express.js is a popular framework built on Node.js for developing web and mobile applications.
2. Python
Python’s simplicity and readability make it a favorite among developers. Frameworks like Django and Flask are widely used for backend development, offering robust features and easy integration with databases.
3. Ruby
Ruby, coupled with the Rails framework, is known for its convention over configuration philosophy, which accelerates development. It’s a solid choice for building web applications quickly and efficiently.
4. PHP
PHP has been around for decades and powers a significant portion of the web, including WordPress. Frameworks like Laravel and Symfony offer elegant syntax and powerful features for building robust applications.
Database Management
Databases are crucial for storing and retrieving data. Fullstack developers must be proficient in both SQL and NoSQL databases:
- SQL Databases: Structured databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite use SQL (Structured Query Language) for data manipulation.
- NoSQL Databases: Unstructured databases like MongoDB and CouchDB offer flexibility, storing data in JSON-like formats.
Tools and Technologies
Fullstack development involves a plethora of tools to streamline workflows and improve productivity:
1. Version Control Systems
Git is the most popular version control system, allowing developers to track changes, collaborate on projects, and manage code repositories. Platforms like GitHub and GitLab provide additional features like issue tracking and CI/CD pipelines.
2. Package Managers
Package managers simplify the installation and management of dependencies. NPM (Node Package Manager) and Yarn are widely used in the JavaScript ecosystem, while Pip is the go-to for Python developers.
3. Build Tools
Build tools automate repetitive tasks like minification, compilation, and testing. Webpack, Gulp, and Parcel are common choices for frontend development.
4. Deployment Platforms
Modern web applications often use cloud services for deployment. Platforms like Heroku, AWS, and DigitalOcean provide scalable solutions for hosting applications, managing databases, and ensuring high availability.
Best Practices for Fullstack Development
To excel in fullstack development, it’s essential to follow best practices:
- Write Clean Code: Adhere to coding standards and guidelines. Use meaningful variable names, write modular code, and comment where necessary.
- Test Thoroughly: Implement unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end tests to ensure your application functions as expected.
- Optimize Performance: Focus on both frontend and backend performance. Minimize HTTP requests, optimize images, and use efficient algorithms for data processing.
- Stay Updated: The tech landscape evolves rapidly. Stay informed about the latest trends, tools, and best practices by following blogs, attending conferences, and participating in online communities.
Becoming a Fullstack Developer: Learning Path
Embarking on a journey to become a fullstack developer involves continuous learning and practice. Here’s a suggested learning path:
- Master the Basics:
- Learn HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Build simple static websites to practice your skills.
- Dive into Frontend Frameworks:
- Explore React, Angular, or Vue.js.
- Develop dynamic and interactive web applications.
- Learn Backend Technologies:
- Choose a backend language (Node.js, Python, Ruby, or PHP).
- Understand server-side logic and database integration.
- Explore Databases:
- Get comfortable with both SQL and NoSQL databases.
- Practice building and querying databases.
- Utilize Development Tools:
- Familiarize yourself with Git, package managers, and build tools.
- Learn to deploy applications using cloud platforms.
- Build Projects:
- Apply your knowledge by building real-world projects.
- Contribute to open-source projects to gain experience and showcase your skills.
FAQs
Q: What is a fullstack developer? A: A fullstack developer is skilled in both frontend and backend development, capable of building complete web applications from start to finish.
Q: Do I need to learn both frontend and backend technologies to become a fullstack developer? A: Yes, fullstack developers need to be proficient in both areas to handle the complete development process.
Q: Which programming languages should I learn for fullstack development? A: Key languages include HTML, CSS, JavaScript (for frontend), and Node.js, Python, Ruby, or PHP (for backend).
Q: How long does it take to become a fullstack developer? A: The timeline varies, but with consistent effort, you can gain a solid foundation within 6-12 months. Continuous learning is essential due to the rapidly evolving tech landscape.
Q: Are fullstack developers in demand? A: Yes, fullstack developers are highly sought after due to their versatility and ability to handle both frontend and backend tasks.
Wrapping Up
Fullstack web development is a dynamic and rewarding field. By mastering both frontend and backend technologies, you can create powerful and efficient web applications. Remember, the journey to becoming a proficient fullstack developer involves continuous learning and practice. Stay curious, build projects, and keep up with the latest trends to excel in this exciting field.